Lab 5 - Memory Allocation Algorithms
Prerequisite Skills for This Lab
- Understand memory allocation from notes, see slides.
- C Skills
- Able to work with a C linked-list.
- Able to create and use structs.
- Able to use pointers: type cast, dereference, pointer arithmetic.
- Able to compile, run, and debug C programs.
Part 1
In a file name lab5.c, you will complete the code below to make it:
- First-fit block selection.
- Best-fit block selection.
- Worst-fit block selection.
- Printing out block IDs.
Copy and paste the following code into your lab5.c file. See "Copy" button on right.
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct header {
uint64_t size;
struct header *next;
int id;
};
void initialize_block(struct header *block, uint64_t size, struct header *next,
int id) {
block->size = size;
block->next = next;
block->id = id;
}
int find_first_fit(struct header *free_list_ptr, uint64_t size) {
// TODO: Implement first fit
return -1;
}
int find_best_fit(struct header *free_list_ptr, uint64_t size) {
int best_fit_id = -1;
// TODO: Implement best fit
return best_fit_id;
}
int find_worst_fit(struct header *free_list_ptr, uint64_t size) {
int worst_fit_id = -1;
// TODO: Implement worst fit
return worst_fit_id;
}
int main(void) {
struct header *free_block1 = (struct header*) malloc(sizeof(struct header));
struct header *free_block2 = (struct header*) malloc(sizeof(struct header));
struct header *free_block3 = (struct header*) malloc(sizeof(struct header));
struct header *free_block4 = (struct header*) malloc(sizeof(struct header));
struct header *free_block5 = (struct header*) malloc(sizeof(struct header));
initialize_block(free_block1, 6, free_block2, 1);
initialize_block(free_block2, 12, free_block3, 2);
initialize_block(free_block3, 24, free_block4, 3);
initialize_block(free_block4, 8, free_block5, 4);
initialize_block(free_block5, 4, NULL, 5);
struct header *free_list_ptr = free_block1;
int first_fit_id = find_first_fit(free_list_ptr, 7);
int best_fit_id = find_best_fit(free_list_ptr, 7);
int worst_fit_id = find_worst_fit(free_list_ptr, 7);
// TODO: Print out the IDs
return 0;
}Sample output
The ID for First-Fit algorithm is: 2
The ID for Best-Fit algorithm is: 4
The ID for Worst-Fit algorithm is: 3Hints
-
Hint: Start with first fit
Implement thefind_first_fit()function first because it's the simplest. Test it well before moving on. -
Hint: Not found
Ensure your algorithms can handle if there's no free block big enough for the new needs. -
Hint: Linked List
The bulk of your work is traversing a linked list! Think about the pointers, and ensure you don't corrupt the linked list in your code! -
Hint: Memory Sanitizer
When working with pointers, you should always turn on memory sanitizer features in the compiler. Compile like:
clang lab5.c -fsanitize=address -
Hint: Stuck on algorithm?
If you are stuck coming up with an algorithm, draw it out on paper and think about all the pointers and header information you have available.
Part 2: Coalescing Contiguous Free Blocks
Write a pseudo-code algorithm for the coalescing contiguous free blocks.
- Write your algorithm is comments at the end of your
lab5.cfile. - As an example, test your algorithm on a memory layout like this, after the red block (z) is freed.
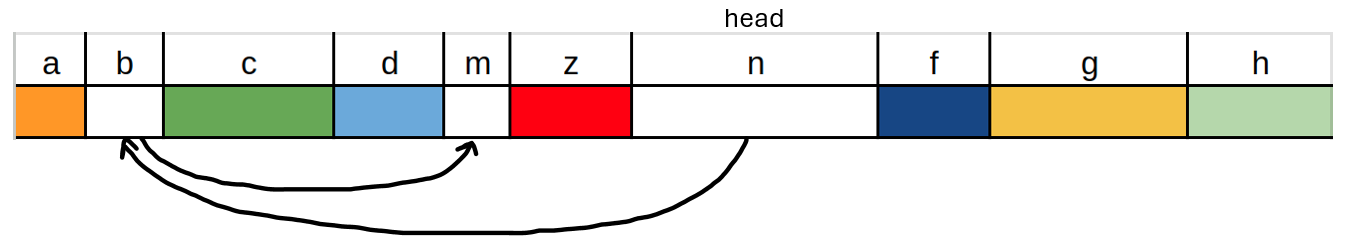
-
Hint - Newly Freed Block
Your algorithm should handle a single newly freed block. If you assume the current link-list of free blocks has been coalesced, then you only need to consider merging the single newly freed block to existing blocks in the linked-list. -
Hint - Before and After
Make sure your algorithm considers that an existing free block may be immediately before, after, or before-and-after the newly freed block. - You do not need to implement this algorithm in C.
3. Reviewing (15 mins)
- During the last 15 minutes of the in-person lab, TAs will show a sample solution.
- TAs will talk through how the solution works and discuss its implementation.
- Discussion Points
- How does the code work?
- What is the memory layout?
- What is being done each iteration of the loops?
- How does the coalescing algorithm work?
- How does the code work?
- Now that you have seen the solution:
- Finish implementing your solution: don't just copy the solution, but it is OK if you use the ideas you saw to help you finish.
- Revise your solution to improve it based on what you learned.
4. Optional Challenges
- Optional: Implement your coalescing algorithm!
- Optional: Test your implementation with a larger data set. Randomly create new blocks, allocate them, and free them. Can you make it crash?
Submission
Submit your lab5.c C code to CourSys; the file name must be an exact match to what CourSys is expecting, otherwise it won't accept it.
Submissions will be marked for completion. It must be valid C code that runs (however we are unlikely to actually compile and run the code). You do not need to complete any optional steps.